How to efficiently reduce hosting energy consumption & carbon footprint

Data centers are gaining increasing importance as an indispensable part of modern computing infrastructures. According to Researches and Markets, the Global Data Center Infrastructure market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.79% during the forecast period, reaching a total market size of US$230.169 billion in 2025 from US$155.201 billion in 2019.
Data centers are physical facilities where computing and networking equipment are located and centralized. They host servers and associated components, such as storage systems and network communications. The main role of a data center is to collect, store, process, and distribute large amounts of data.
Over the years, data centers have evolved from centralized on-premises facilities to edge deployments to public cloud services, and they are now critical components of modern IT infrastructure. However, this growth in importance is also accompanied by increasing concern regarding the energy consumption of these facilities. In total, the global internet consumes 416.2 terawatt-hours of electricity per year, which is more electricity than the whole of the United Kingdom. This translates into large amounts of carbon emissions. In fact, 2% of global carbon emissions come from the electricity used by the internet, which is mainly consumed by data centers.
According to widely cited energy forecasts, the total electricity demand of information and communication technology (ICT) will accelerate in the 2020s, and data centers will take a larger slice. This implies that their environmental impact will increase as well. If we add to that the rising energy costs, it becomes obvious that businesses and organizations need to efficiently address data centers’ energy consumption issues in order to cut costs and promote environmental responsibility.
On average, servers and cooling systems account for the greatest shares of direct power use in data centers as shown in the figure below.
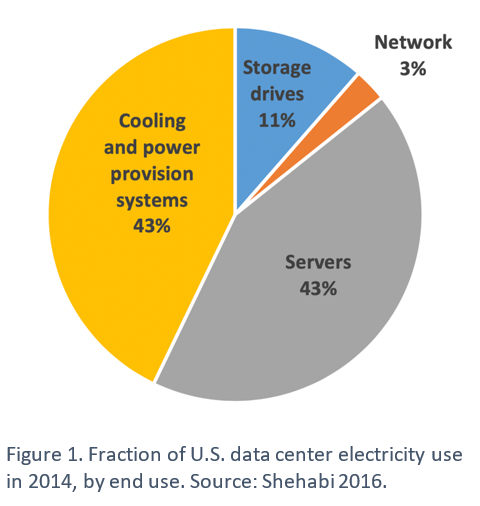
The volume of workloads that a data center processes and the total number of servers required to process the workloads are the main factors that determine how much energy those servers will consume. However, so much energy is wasted due to the fact that servers run idle or at low utilization. Servers usually don’t employ any energy-saving mechanisms like spin-down idle disks or standby, and 60% of a typical database server’s peak energy is consumed when idle.
With that in mind, let’s look at some of the efficient ways that can help reduce servers’ energy consumption.
Consolidating and virtualizing servers to maximize server utilization
Most physical servers run at about 5% to 15% utilization, yet they draw full power. In order to increase server utilization and reduce wasted energy, most companies and organizations use server consolidation and virtualization.
Server virtualization aims at reducing electrical consumption by lowering the number of physical servers. Virtualization is the process of creating and abstracting multiple virtual servers on a single physical server host via software, each virtual server runs independently. This operation is done using a hypervisor that serves as a platform for the virtual servers’ operating systems while keeping the environments totally private and separate from each other.
Virtualization and consolidation go hand in hand, and that’s because the former is the enabler of the latter. Consolidating multiple, independent servers to a single physical server enables those servers to operate more efficiently and reduces energy costs by up to 80%.
Killing zombie / comatose servers
Replacing old servers with new, more energy-efficient hardware servers
Reducing website energy consumption
- Image optimization
Images account for about 50% of the average web page’s file size. reducing images’ size can result in a big reduction in the amount of data that a server needs to transmit. This in turn reduces the amount of energy consumed by the server and speeds up load times. - Gzip compression
Gzip compression reduces a website’s file size by up to 70%. As a result, the server takes less time and consumes less energy to transmit them. - Reducing video
Video provides a more engaging user experience. However, it is by far the most processing-intensive and data-intensive form of content. When having a certain number of videos on the website is really necessary, the number of streaming videos can be reduced by removing the video auto-play function and by keeping those videos short. - Page or HTTP caching
Page caching aims at reducing the processing work that a server needs to perform in order to serve up a website. It works by temporarily storing website data such as JavaScript files, images, stylesheets, and similar content when a web page is loaded for the first time so it can quickly load that content when that page is visited again. This makes the website load faster and saves bandwidth and energy. - Code minification
Caching might not be enough to decrease the loading time of a web page, that’s where code minification comes in. Code, meaning JS, HTML, and CSS, minification is an optimization technique that reduces the size of JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files by stripping out comments, unnecessary whitespace, line-breaks, or extra characters from the source code. Code optimization also eliminates round-trip data transfer by reducing HTTP requests. Once minified, files become lighter, and transferring them becomes faster and less energy-intensive. - Using AMP
Mobile accounts for approximately half of the web traffic worldwide (54.8% of global website traffic), which means that websites need to load fast on mobile devices as well. AMP (accelerated mobile pages) is a technology that strips out unnecessary code and file weight to make content load faster on mobile devices. It delivers a minimalist, more energy-efficient version of the original web page to mobile users. - Fonts optimization
Typography has a significant impact on good web design. Webfonts allow text to be zoomable, selectable, and searchable. They also provide sharp and consistent rendering on screens with different sizes and resolutions. However, web fonts impact HTTP requests, page weight, and website speed and thus need to be optimized. In fact, a single font file could be as much as 250kb. Minimizing the size of a website's fonts can reduce file size by up to 97%. Optimizing fonts can be done by using FontLoading API to optimize the critical rendering path, using modern web font file formats like WOFF and WOFF2, etc.